ITAD Compliance 101: What Every Business Should Know About Asset Disposal

Image Source: freepik.com/freepik
Do IT assets that once held client records, employee details, and financial data stop being a liability when no longer in use? The truth is, retired tech, if mishandled, can expose your company to fines, reputational damage, and even legal trouble.
Data from real-world audits also shows how risky improper business asset disposal can be. One investigation uncovered over 300,000 recoverable files on 85 used devices purchased secondhand for $600.

The statistics about the cost of file recovery for used devices
Every piece of technology in a business, such as laptops, servers, and hard drives, eventually reaches the end of its life. Disposing of those retired techs is more complicated than it used to be. In 2024 alone, global e-waste hit 62 million metric tons, and less than 20% of it was formally recycled. This gap raises environmental concerns and also poses serious data security and ITAD compliance issues for businesses.

The global e-waste generated in 2024 was 62 million metric tons, with 20% yet to be recycled.
When companies offload old IT equipment without a proper plan, they often overlook critical steps that protect sensitive data and regulatory compliance. This calls for proper IT asset disposition, also known as ITAD. It’s a process that helps businesses retire technology safely, responsibly, and in line with the law.
Here’s everything you need to know about protecting your organization long after the hardware stops working.
ITAD and Its Key Components
IT Asset Disposition, or ITAD, is the structured approach businesses use to retire aging technology in a way that’s secure, responsible, and aligned with compliance standards. As companies upgrade systems and scale operations, getting rid of older devices becomes more important than ever.
ITAD is an umbrella term that comprises various key elements for a solid asset disposal process.
Data Destruction

Definition of data destruction of sensitive data
Above all else, data security should never be compromised. Before any device leaves your hands, all sensitive data must be permanently erased. This might involve software-based data wiping, physical destruction of drives, or methods such as degaussing or cryptographic erasure, depending on your risk level and industry-specific requirements.
Reuse and Recycling

The major difference between reusing and recycling
Instead of sending assets for disposal straight to the landfill, ITAD encourage the recovery of usable components like glass, metals, plastics, and reintroduces them into the supply chain. This reduces environmental harm and often allows businesses to recover some value from obsolete assets.
Refurbishment

The meaning of refurbishment is to bring the device to working condition
Not every device needs to be scrapped. Equipment that is still functional, even if a bit outdated or damaged, can often be repaired and refurbished. Many ITAD providers offer this service to help you extend the lifespan of tech and support more sustainable operations.
Compliance

This is what compliance means: meeting the industry standards.
ITAD data security compliance is a legal requirement in many industries. Whether it’s GDPR, SERA, or other local data protection and environmental laws, the IT asset disposal process ensures your business meets all necessary regulations when disposing of electronic equipment. Documentation and traceability are key here, especially for audits.
Business Asset Disposal Relief
When old IT assets are sold as part of a business wind-down or restructuring, business asset disposal relief (BADR) may apply. This is particularly relevant for companies navigating a small-business-restructuring-process, where the sale of assets is often a key step. BADR offers a reduced 10% Capital Gains Tax rate on qualifying assets. It’s commonly used by business owners selling shares or equipment during such transitions. However, business asset disposal relief limits apply; the lifetime cap is currently set at £1 million per individual, beyond which standard tax rates are charged.
ITAD Trends and Statistics
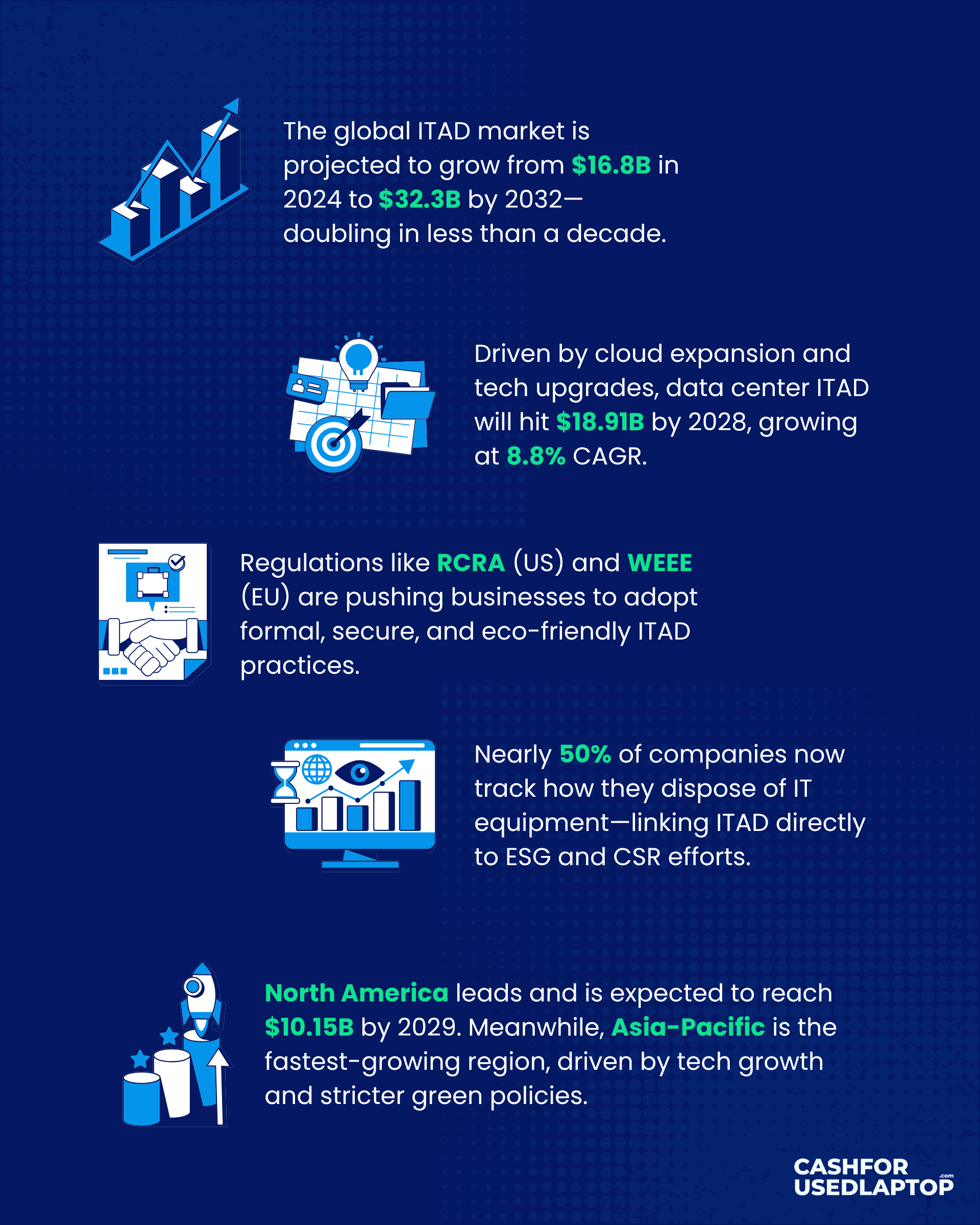
Infographic that displays various statistics and trends of ITAD
-
The global ITAD market is projected to grow from USD 16.8 billion in 2024 to USD 32.3 billion by 2032, more than doubling in under a decade.
-
The data center ITAD segment alone is expected to increase from USD 12.42 billion in 2023 to USD 18.91 billion by 2028, with a CAGR of 8.8%, driven by cloud growth and large-scale hardware turnover.
-
Tighter rules from regulatory bodies like the RCRA (US) and WEEE Directive (EU) are pushing businesses to adopt formal ITAD practices that prioritize both environmental and data security standards.
-
Nearly 50% of organizations now require reporting on IT equipment disposal as part of their sustainability metrics, linking ITAD directly with ESG and CSR initiatives.
-
North America currently leads the ITAD market and is expected to hit USD 10.15 billion by 2029. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, thanks to evolving tech landscapes and stronger environmental policies.
How the ITAD Process Works
No two businesses approach IT asset disposal in the same way. Some deal with a few laptops; others are phasing out entire server rooms. Hence, there isn’t a fixed asset disposal process.
Still, the general flow remains consistent, starting with identifying what needs to go and ending with making sure it’s all handled securely and responsibly.
A well-run IT asset disposal process helps prevent data leaks, supports compliance, and even recovers some of the investment from retired tech. Below are the key stages companies should follow when retiring their IT assets.
Review and Access What You Have
Before anything gets wiped or shipped out, you need a clear picture of what’s actually being retired. That means pulling together a detailed list of all the IT equipment you plan to dispose of, including laptops, servers, external drives, and even networking gear.
Prioritize the asset disposal journal entry and record details like the model, serial number, condition, and whether the device is still operational. It helps prevent anything from slipping through the cracks and sets the tone for the rest of the process. A solid inventory helps with planning and makes reporting and compliance much easier down the line.
Wipe the Data
Once the devices are accounted for, your top priority is the data. Simply deleting files isn’t enough; data can still be recovered unless it’s properly wiped. Depending on your industry and risk tolerance, this could mean secure data erasure software, degaussing magnetic storage, or physical destruction of the drives.
Whichever method you choose, it needs to be certified and documented. Failing to sanitize data properly can open the door to security breaches or regulatory trouble, even after the equipment leaves your building. This step is non-negotiable for any business handling sensitive or regulated information.
Evaluate the Value of Your Assets
Not every retired device belongs in a recycling bin. Some of your equipment might still hold value, especially if it’s only a few years old or in good condition. This is where asset evaluation comes in. By working with an ITAD compliance vendor or using in-house benchmarks, you can determine your device’s resale value and know what can be refurbished.
You can also consider donating, for instance, a laptop that might be useless to you may be the best laptop for students. Even if you’re not looking to turn a profit, recouping some of the original investment is always a plus. It also helps reduce waste and keeps useful technology in circulation longer, which supports your organization’s sustainability goals.
Ensure Secure Transportation
Once everything is sanitized and sorted, the next step is moving the equipment safely. This might sound simple, but secure transportation is crucial. Devices that still contain data, even after wiping, can still be vulnerable during transit.
Many ITAD providers offer secure pickup and transport services with chain-of-custody tracking to ensure nothing is lost or tampered with. Depending on your setup, the data destruction may even happen at the vendor’s facility, not on-site. Either way, it’s essential to choose a provider with a strong reputation for secure logistics.
Recycle and Dispose Securely
At the end of the process, some equipment just won’t be reusable. When that’s the case, proper recycling is the responsible route. Responsible recycling can turn tech trash into treasure. Certified ITAD providers follow strict environmental guidelines to ensure that materials, such as plastics, metals, and circuit boards, are recovered wherever possible and that nothing hazardous ends up in landfills.
This IT asset disposal process doesn’t exist simply to tick the sustainability box. It’s your duty as a business to reduce the environmental impact. With the right provider, you’ll also receive documentation that proves everything was disposed of in accordance with industry and legal standards.
Why ITAD Matters
Upgrading company tech is routine, but what happens to the old equipment matters just as much. ITAD deserves a place in the business strategies of businesses of all sizes. Here’s why you shouldn’t skip it.
Keeps Your Data Secure

This statistic talks about the average cost of a data breach in 2023
Obsolete doesn’t mean harmless. Retired devices still hold sensitive information that can fall into the wrong hands and lead to costly breaches. In 2023, the average data breach cost hit $4.45 million. For example, Filefax, a medical records firm, was fined $100,000 after it left patients’ files in an unlocked truck, compromising data for over 2,000 individuals.
Stay Legally Compliant
Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and WEEE have clear expectations for how businesses must handle old IT. A poorly handled device can trigger hefty penalties. In the Filefax case mentioned above, even though the company had shut down, it was still held legally accountable under HIPAA for how those records were discarded.
Saves Money and Recovers Value

The value of the recycling market in 2022 and the projection for 2030.
A properly executed asset disposal process can generate returns. Assets can be remarketed, refurbished, or reused, putting some money back into your IT budget. At the same time, it helps avoid fines and reputational costs tied to non-compliance or data loss.

Xerox reports the savings that are made possible with take-backs and recycling programs.
Protect the Planet

Recycling a ton of e-waste can save 20,000 kWh
Electronic waste is one of the fastest-growing pollution problems in the world. With a solid ITAD compliance plan, you can help reduce landfill waste, recover valuable materials, and support greener business practices. It’s good for the planet, and it reflects well on your brand.
Choose the Best ITAD Provider!
The bottom line is finding the right ITAD provider to make sure your assets for disposal are handled securely, ethically, and in line with regulations. Here’s what to look for:
-
Go through verified customer feedback
-
Make sure the provider complies with all the relevant environmental laws in your region
-
Look for certifications like R2, e-Stewards, or WEEE to ensure they follow ethical practices
-
Visibility into your assets from collection and tracking to final disposal
-
Audit trails for any future proof of proper disposal, particularly during checks or investigations
Find and work with a reputable partner to ensure a secure overall process from ITAD compliance and data destruction to responsible laptop recycling. The right ITAD vendor will ensure you retire your devices in a way that protects the environment and aligns with your company‘s values.


